Why Losing Weight Fast Isn't a Good Idea, and What to Do Instead

Everyone wants a quick fix when it comes to weight loss. The allure of shedding pounds rapidly is hard to resist, especially with the countless diets promising just that. But here's the truth: anything that sounds too good to be true usually is.
Rapid weight loss may seem tempting, but it comes with its own set of dangers and drawbacks. So, let's take a closer look at why losing weight fast isn't a good idea and explore what you can do instead to achieve your goals in a safe and sustainable manner.
What is Considered Fast Weight Loss?
Fast weight loss is typically defined as a 5 percent reduction in body fat within five weeks. This translates to around one or more kilos per week, depending on an individual's body weight. However, a healthy rate of weight loss is considered to be 0.25 to 0.7 kg per week, with an ultimate goal of losing 5-10 percent of your total body weight within the first six months. So, it's important to recognize that slow and steady progress is key when it comes to achieving long-term success.
Why is Rapid Weight Loss Dangerous?
Rapid weight loss can be dangerous for several reasons. Let's explore some of the evidence-backed risks associated with losing weight too quickly.
- Loss of Lean Muscle Mass:
Weight loss doesn't necessarily mean losing body fat. Rapid weight loss often results in the loss of lean body mass, such as muscle, organ tissues, or water weight. This can have negative consequences for your health, including fatigue, increased risk of injury, low energy levels, reduced metabolism, and a decline in neuromuscular function. Preserving lean muscle is crucial to shifting your body composition and ensuring that you primarily lose body fat. - Promotes Disordered Eating Behaviors:
Crash diets and extreme weight loss plans are often restrictive in nature, leading to unhealthy eating habits. Moreover, studies have shown that the more extreme a diet is, the more likely it is to be discontinued prematurely. Restrictive diets that promote rapid weight loss have been linked to negative psychological effects, including disordered eating behaviors and orthorexia (an obsession with healthy eating). Maintaining a healthy relationship with food and avoiding restrictive diets is essential for preventing these issues. - Potential Use of Unsafe Supplements, Products, or Medications:
Many individuals resort to risky measures to achieve rapid weight loss, including the use of unsafe supplements, products, or medications. Prescription drugs designed for weight loss can have side effects such as fatigue, dry mouth, hair loss, and high blood pressure. Additionally, over-the-counter weight loss supplements are often poorly studied and can be dangerous. It's crucial to consult a healthcare professional before considering any weight loss medications or supplements.
6 Science-Backed Ways to Safely Promote Weight Loss
Now that we understand the risks associated with losing weight too fast, let's focus on safe and sustainable strategies to achieve your weight loss goals. Here are six science-backed methods you can incorporate into your lifestyle:
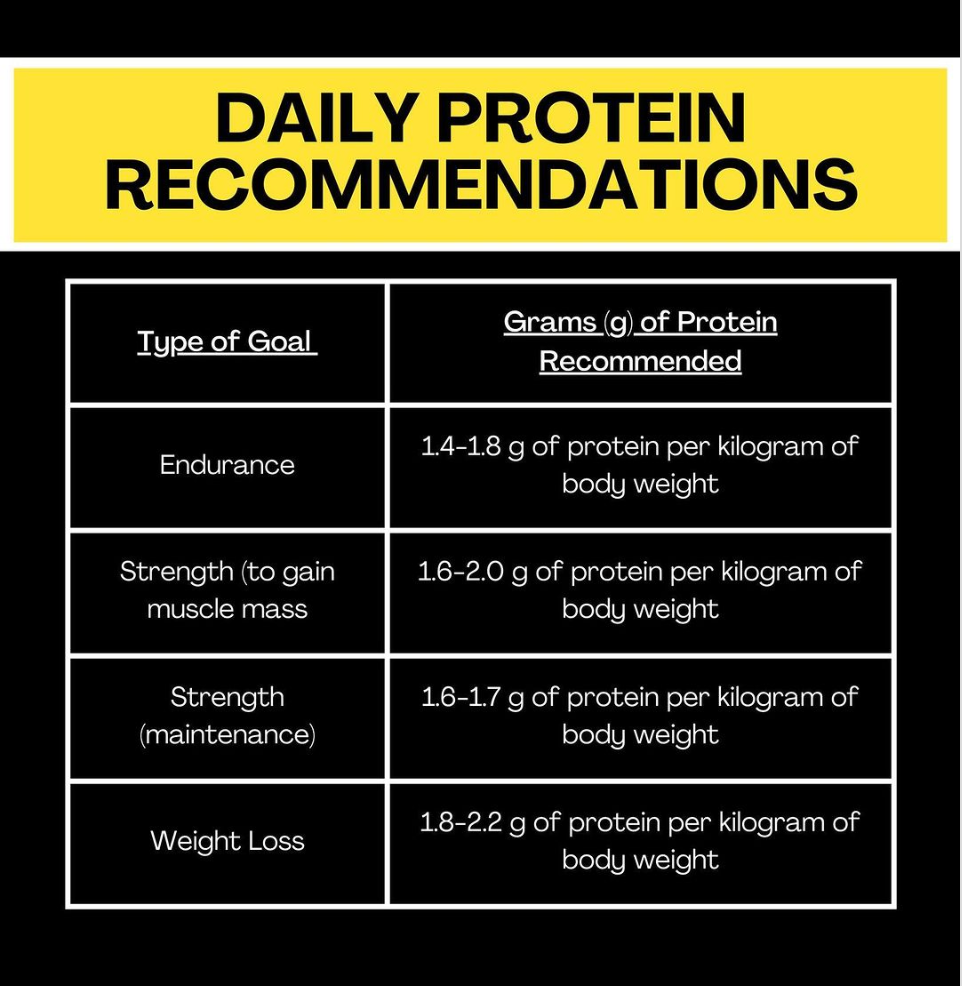
- Prioritize Protein:
Including an adequate amount of protein in your diet is crucial for weight loss. Aim for a variety of lean protein sources such as fish, nuts, and chicken while reducing your intake of processed cold cuts and fatty cuts of beef. High protein diets increase satiety, reduce overall caloric intake, and promote fat loss. They also help preserve lean muscle mass and maintain an efficient metabolic rate during weight loss.
2. Make Sleep a Priority:
Quality sleep plays a vital role in successful weight loss. Aim for at least 7 hours of uninterrupted sleep per night. Reduce screen time before bed, avoid consuming caffeine in the afternoon and evening, and engage in regular physical activity to improve your sleep quality.
3. Find Ways to Reduce Stress:
Stress can hinder weight loss progress. Implement stress management techniques such as meditation, taking walks, reading, taking baths, engaging in hobbies, deep breathing exercises, and regular exercise. Working towards reducing stress on a daily basis can have a positive impact on your weight loss journey.
4. Create a Small Calorie Deficit:
While a calorie deficit is necessary for weight loss, it's important to find the right balance. Instead of drastically reducing your daily caloric intake, aim for a moderate reduction of around 250 calories per day. Combining exercise and diet is an effective way to create a calorie deficit. Additionally, focus on increasing your daily energy expenditure through exercise, the thermic effect of food (TEF), and non-exercise activity thermogenesis (NEAT).
5. Focus on Fiber:
Incorporate high-fiber foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables into your diet. These foods are more satisfying, leading to the consumption of fewer calories overall. High-fiber whole foods should be favored over fiber supplements. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables has additional benefits for cardiovascular and cancer risk factors. The recommended daily intake of fiber is 25 grams for women and 38 grams for men.
6. Incorporate Strength Training: Engage in resistance or strength training exercises 2-3 days per week alongside aerobic workouts. Resistance training not only promotes weight loss but also improves body composition by reducing body fat and increasing muscle mass. If you don't have access to a personal trainer, there are various apps and at-home streaming workouts available to help you incorporate strength training into your routine.
By following these safe and science-backed strategies, you can achieve sustainable weight loss while preserving lean muscle mass and promoting overall well-being.
In conclusion, losing weight too fast is not a healthy approach. It can result in the loss of lean muscle mass, promote disordered eating behaviors, and involve the use of unsafe supplements or medications. Instead, focus on incorporating safe and sustainable practices into your lifestyle. Prioritize protein, make sleep a priority, find ways to reduce stress, create a small calorie deficit, focus on fiber-rich foods, and incorporate strength training. Remember, slow and steady wins the race when it comes to long-term weight loss success.