The Science Behind Taste and Sugar Cravings

I recently came across a fascinating discussion between Andrew Huberman and Dr. Charles Zuker on the power of taste and its impact on our dietary choices, I couldn't help but delve deeper into the science behind it. In this blog post, I aim to explain the intricate neural circuits involved in taste perception and the gut-brain axis, and how we can utilize this knowledge to lead healthier lives.
Defining Perception and Taste:
Perception is our brain's way of interpreting sensory cues and making sense of the world around us. It categorizes our responses into seeking, avoiding, or tolerating, depending on how we interpret the information received. Taste, on the other hand, is a complex system that involves the computation, encoding, and decoding of sensory information.
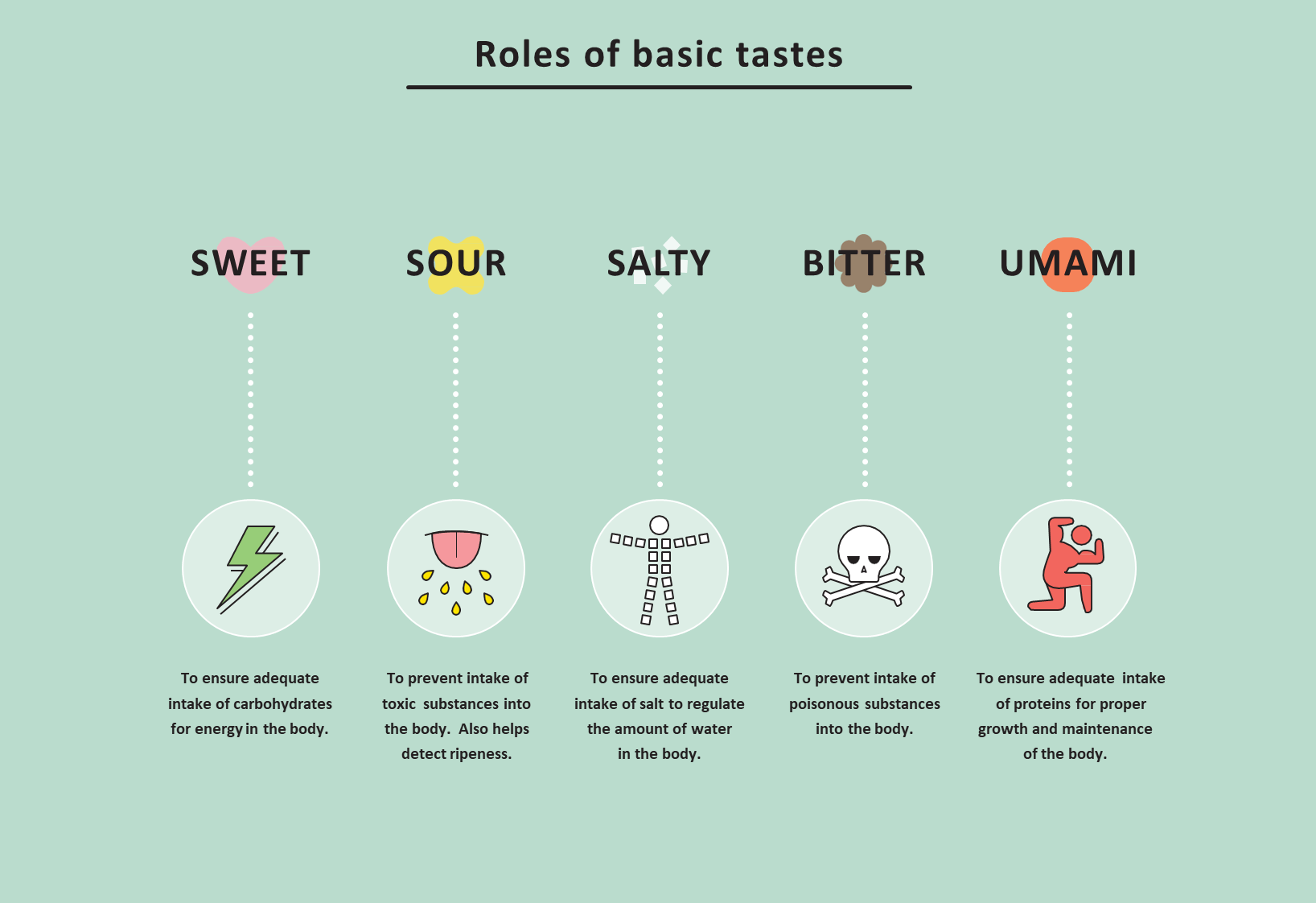
Humans can detect five basic tastes: sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami. Each taste serves a specific purpose in our diet, such as providing energy (sweet), maintaining electrolyte balance (salt), or signaling the presence of potentially harmful substances (bitter). Contrary to popular belief, taste receptors are not limited to specific regions of the tongue. Rather, every taste bud in our oral cavity contains receptors for all five basic tastes.
Understanding the Addictive Nature of Sugar and the Gut-Brain Axis:
Sugar holds a unique position in our dietary preferences due to its addictive nature. The perception and craving for sugar occur in multiple stages. When sugar receptors on our tongue are activated, we initially experience a pleasurable sensation. However, as these receptors become desensitized, the craving for more sugar intensifies.
The gut-brain axis plays a significant role in driving our preference for sugar. It involves the communication between our gut and brain, reinforcing our desire for certain foods. Sugar activates the reward-pleasure centers in our brain,leading to changes in our internal state.
Even if the sweet receptors on the tongue are removed, studies have shown that the preference for sugar can persist due to learned behavior and detection through other senses like smell and location.
Processed Foods and their Impact on the Gut-Brain Axis:
Highly processed foods present a significant challenge to our health and dietary choices. These foods have the ability to hijack the gut-brain axis, continuously reinforcing cravings and leading to overconsumption. By breaking down food into easily digestible forms, processed foods bypass the natural mechanisms that regulate satiety, making it easier to overeat.
Dr. Zuker highlights that diseases of malnutrition today are often linked to overnutrition rather than the absence of food itself. The continuous reinforcement of "wanting" through the gut-brain axis perpetuates unhealthy eating habits and contributes to the global obesity epidemic.
Using Knowledge to Make Healthier Choices:

Now that we understand the science behind taste perception and the influence of processed foods on the gut-brain axis, we can make informed dietary choices to improve our health.
Here are a few ways we can apply this knowledge in our daily lives:
- Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods: Opt for natural, nutrient-dense foods that nourish our bodies and provide a range of tastes and flavors.
- Limit added sugars: Be mindful of the amount of added sugars in your diet and try to reduce consumption. Gradually train your taste buds to appreciate foods with less sweetness.
- Listen to your body's signals: Pay attention to your body's cues of hunger and fullness. Allow yourself to eat when genuinely hungry and stop eating when satisfied, rather than relying on external cues or cravings.
- Explore diverse flavors: Experiment with a variety of tastes and flavors to enhance your eating experience. Incorporate different herbs, spices, and healthy seasonings to make whole foods more appealing.
- Practice mindful eating: Slow down and savor each bite. Engage your senses, appreciate the flavors, textures, and aromas of your food. This can help you enjoy your meals more and tune in to your body's signals.
By understanding the science behind taste perception, cravings, and the impact of processed foods on our health, we can make conscious choices to improve our overall well-being. By prioritizing whole, unprocessed foods, reducing added sugars, and practicing mindful eating, we can foster healthier habits and enjoy a more balanced diet. Let's empower ourselves with this knowledge and take steps towards a healthier, more fulfilling life.
If you're looking for personalized guidance and support on your journey towards a healthier lifestyle, I'm here to help. Feel free to reach out to me at bjpcoetzer@me.com. Whether you have specific questions, need advice, or want assistance in creating a tailored plan, I'm dedicated to supporting you in achieving your health goals.
Remember, making positive changes to your diet and lifestyle is a gradual process. It's about finding what works best for you and making sustainable choices. Together, we can take steps towards a healthier, happier life.