The Benefits of Fiber for Optimal Digestion and Weight Management

In recent years, there has been a growing awareness of the importance of fiber in a healthy diet. Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that cannot be digested by the body, but it plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal digestive health and promoting healthy weight management. In this article, we will explore the various benefits of consuming fiber, including its impact on digestion and weight management, as well as practical tips for incorporating more fiber into your daily diet
What is Fiber?
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot digest. It is found in plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds. There are two types of fiber: soluble and insoluble.
Soluble fiber dissolves in water and forms a gel-like substance in the digestive system. This type of fiber can help to lower cholesterol levels and regulate blood sugar levels.
Insoluble fiber, on the other hand, does not dissolve in water and helps to add bulk to the stool, promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation.
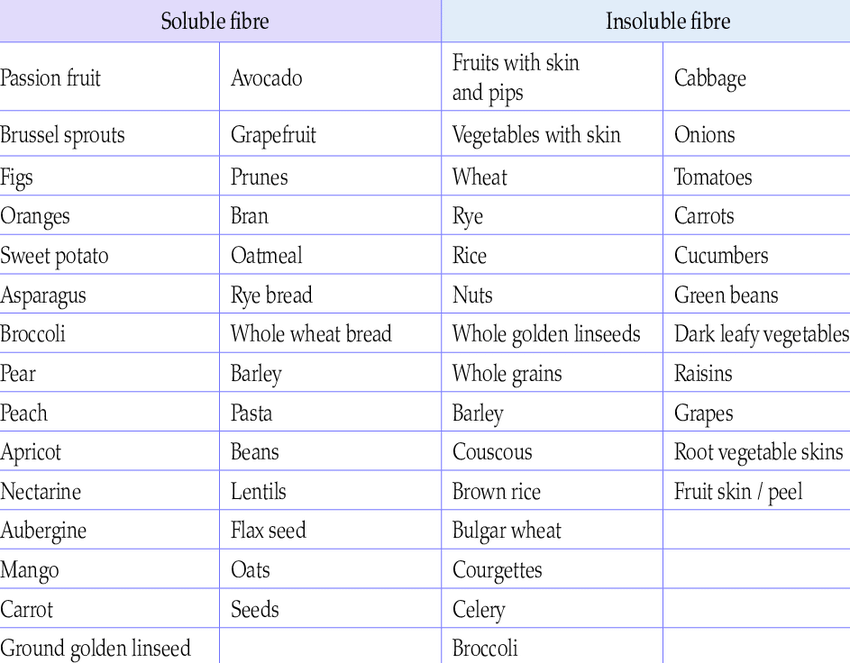
Both types of fiber are important for a healthy diet and can provide numerous benefits for optimal digestion and weight management.
When fiber is consumed, it passes through the digestive system relatively intact, without being broken down by digestive enzymes. Instead, it moves through the gastrointestinal tract, providing bulk and helping to move waste through the colon for elimination.
The Benefits of Fiber for Digestion
Fiber plays a vital role in digestion and can have many benefits for overall gut health. Here are some ways in which fiber can aid in digestion:
Explanation of how fiber aids in digestion: Fiber is not digested or absorbed by the body, unlike other nutrients such as fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. Instead, it passes through the digestive tract largely intact, adding bulk to stools and helping them move through the colon. This helps keep the digestive system running smoothly and prevents constipation.
Benefits of fiber for constipation: Constipation is a common digestive problem characterized by infrequent bowel movements and difficulty passing stool. A diet high in fiber can help prevent and alleviate constipation by adding bulk to the stool, making it easier to pass. This can help regulate bowel movements and promote regularity.
Benefits of fiber for diarrhea: Fiber can also be beneficial for those suffering from diarrhea. Soluble fiber, in particular, can absorb excess water in the digestive tract, which can help solidify loose stools and reduce diarrhea. This type of fiber can also help regulate bowel movements, preventing diarrhea from recurring.
Benefits of fiber for diverticulitis: Diverticulitis is a condition in which small pouches called diverticula form in the walls of the colon and become inflamed or infected. A high-fiber diet can help prevent diverticulitis by keeping the stool soft and preventing strain during bowel movements. In addition, fiber can help reduce inflammation in the colon and promote healing.
Incorporating fiber-rich foods into the diet can be an effective way to improve overall digestive health and prevent digestive problems.
The Benefits of Fiber for Weight Management
Fiber plays a crucial role in weight management, as it helps to control appetite and maintain a healthy weight. Here are some of the benefits of fiber for weight management:
- Appetite Control: Foods high in fiber tend to be more filling and satisfying, which can help to reduce hunger and control appetite. Fiber-rich foods take longer to digest, leading to a longer feeling of fullness and less frequent snacking.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Incorporating high-fiber foods into your diet can help to maintain a healthy weight. Fiber helps to regulate digestion, and studies have shown that those who consume more fiber tend to have a lower body weight.
- Preventing Obesity: Consuming a high-fiber diet has been linked to a reduced risk of obesity. Foods high in fiber can help to reduce overall calorie intake by providing a feeling of fullness and satisfaction while keeping blood sugar levels steady.
It is important to note that simply increasing fiber intake is not a guaranteed solution for weight loss. A balanced diet and regular exercise are also important factors in maintaining a healthy weight.
The Link Between Mental Health and Fiber Intake
While fiber is often associated with physical health benefits, research suggests that there may also be a link between fiber intake and mental health. Studies have found that diets high in fiber may be associated with a reduced risk of depression and anxiety.
One possible explanation for this link is the role of fiber in promoting the growth of healthy gut bacteria. The gut microbiome, which is made up of trillions of microorganisms that live in the digestive tract, has been shown to play a role in brain function and mental health. A healthy gut microbiome is associated with lower levels of inflammation, which has been linked to depression and other mental health disorders.
In addition, fiber-rich foods may also help regulate blood sugar levels and provide a steady source of energy, which can help improve mood and reduce fatigue.
One study published in the Journal of Nutrition found that women who consumed higher amounts of fiber had lower levels of stress and were less likely to experience symptoms of depression. Another study published in the journal Nutritional Neuroscience found that a diet high in fiber was associated with lower levels of anxiety in young adults.
Overall, while more research is needed to fully understand the link between fiber intake and mental health, these studies suggest that consuming a diet high in fiber may have additional benefits beyond physical health.
How to Incorporate Fiber into Your Diet
Incorporating fiber into your diet is important for maintaining a healthy digestive system and managing your weight. Here are some tips on how to increase your fiber intake:
Recommended Daily Intake of Fiber: The recommended daily intake of fiber for adults is 25-30 grams per day. However, most people don't consume enough fiber in their diets, which can lead to digestive problems and other health issues.
High-Fiber Foods: There are many high-fiber foods that you can add to your diet, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts. These foods are also rich in other important nutrients that your body needs to stay healthy.

10 Best Fiber Sources (fiber content per 100g of food):
- Split peas (16.3g)
- Lentils (7.9g)
- Black beans (8.7g)
- Chickpeas (7.6g)
- Artichokes (5.4g)
- Avocado (6.7g)
- Raspberries (6.5g)
- Whole wheat spaghetti (6.3g)
- Chia seeds (34.4g)
- Almonds (12.5g)
Tips for Increasing Fiber Intake:
- Start by adding more fruits and vegetables to your meals and snacks.
- Choose whole grain breads, cereals, and pasta instead of refined grains.
- Replace meat with beans or legumes in your meals a few times a week.
- Snack on nuts and seeds instead of processed snacks.
- Try adding chia seeds or ground flaxseed to your smoothies or yogurt.
Incorporating these high-fiber foods into your diet and making small changes can help you meet your recommended daily intake and improve your overall health. Remember to increase your fiber intake gradually and drink plenty of water to avoid digestive discomfort.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fiber is an essential component of a healthy diet, offering numerous benefits for both digestion and weight management. Consuming enough fiber on a daily basis can lead to improved bowel movements, relief from constipation, and a reduced risk of certain digestive disorders. Fiber can also aid in weight management by promoting feelings of fullness, reducing calorie intake, and preventing obesity.
To incorporate more fiber into your diet, focus on consuming high-fiber foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Aim for the recommended daily intake of fiber, which is around 25-30 grams for most adults. You can also increase your fiber intake by making small dietary changes such as choosing whole-grain bread over white bread, adding berries to your breakfast, or snacking on raw vegetables.
Lastly, it is important to note that increasing your fiber intake may not only benefit your physical health but also your mental health. Several studies have suggested that fiber intake is linked to improved mood and a reduced risk of depression and anxiety. Therefore, consuming a fiber-rich diet may contribute to overall well-being.
In summary, incorporating fiber into your diet is a simple and effective way to improve your digestion, manage your weight, and promote overall health and wellness. By making small changes to your diet, you can easily increase your fiber intake and reap the numerous benefits that come with it.