The Secret Link Between Sleep and Diabetes: How to Lower Your Risk

The Link Between Sleep Deprivation and Diabetes: What You Need to Know
Sleep is essential for maintaining a healthy body and mind. It's during sleep that our bodies repair and restore themselves, and a lack of sleep can have a negative impact on our health.
One area where sleep deprivation has been linked is insulin resistance and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. In this article, we'll explore the science behind this link and provide some tips to help you improve your sleep and reduce your risk of diabetes.
The Science Behind the Link
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate our blood sugar levels. When we eat, our blood sugar levels rise, and insulin helps move that sugar into our cells to be used for energy.
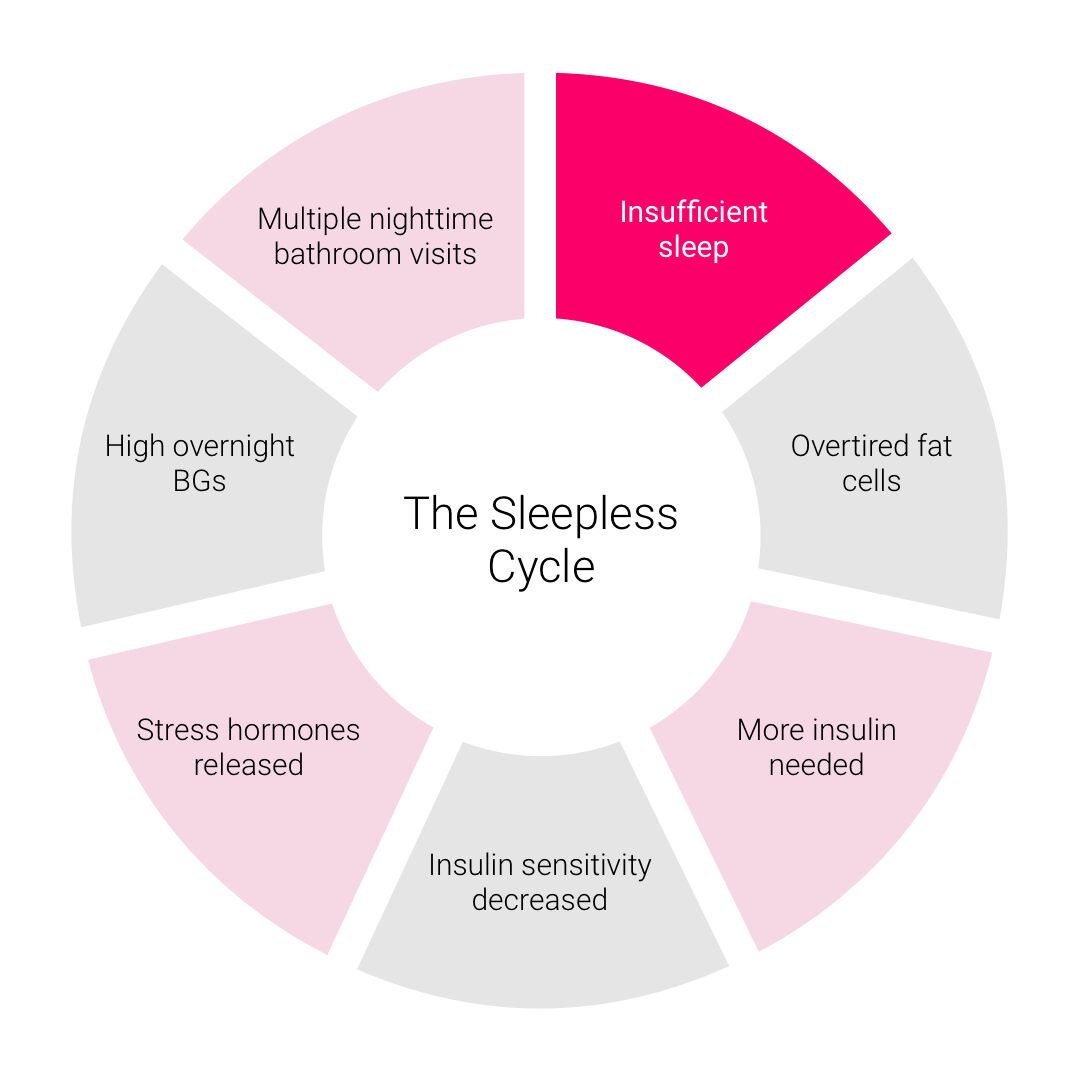
However, when we become insulin resistant, our cells become less responsive to insulin, and our pancreas has to work harder to produce more insulin to keep our blood sugar levels in check.
Recent studies have shown that sleep deprivation can cause insulin resistance, making it harder for our cells to respond to insulin. This means our pancreas has to produce more insulin to keep our blood sugar levels in check, leading to a state of hyperinsulinemia. Over time, this can lead to a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Tips to Improve Your Sleep
If you're struggling with sleep, there are several things you can do to improve your sleep quality and reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes:
- Stick to a Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
- Create a Relaxing Sleep Environment: Make sure your bedroom is dark, cool, and quiet. Remove electronic devices and avoid using screens before bedtime.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and progressive muscle relaxation can help you relax and fall asleep faster.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular exercise can improve sleep quality and help regulate your blood sugar levels.
- Avoid Stimulants: Avoid caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol before bedtime, as they can disrupt your sleep.
- Limit Fluids Before Bedtime: Avoid drinking large amounts of fluids before bedtime to reduce the need to use the bathroom during the night.
Incorporating these tips into your routine can help you improve your sleep quality and reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Remember, sleep is essential for maintaining a healthy body and mind, so prioritize it just as you would a healthy diet and regular exercise.
In conclusion, sleep deprivation can have a negative impact on our health, including an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. By improving your sleep quality through lifestyle changes, you can reduce your risk and improve your overall health and well-being.