The Food Order Formula: How Food Order Impacts Your Health?

Have you ever heard the saying "eat your salad first"? Well, it turns out there might be more to it than just good table manners. The concept of meal sequencing, or eating specific foods in a particular order, has been around for a while, especially in the diabetic community. But here's the surprising part – even if you're not diabetic, the order in which you eat your food can still make a difference. Yes, you read that right!
Meal sequencing offers a range of benefits, including aiding in fat loss, reducing glucose responses, and managing energy intake. In this article, we'll delve into the fascinating world of meal sequencing, explaining why it matters and how it could be the missing strategy in your diet.
Why The Order You Eat Foods Impacts Your Body’s Glucose Response
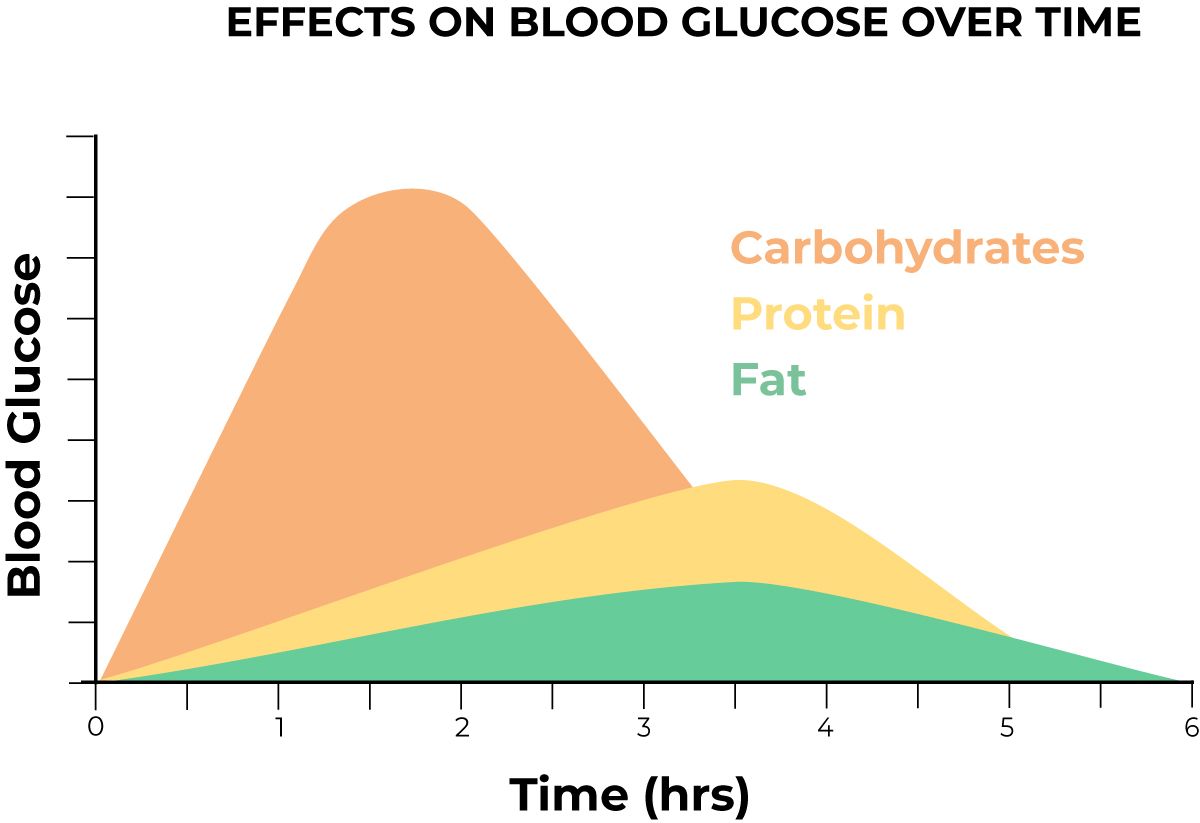
So, what's the connection between food order and your body's glucose response? It all comes down to our human physiology. Carbohydrates, the body's primary source of energy, are broken down into glucose relatively quickly. While this can provide an instant energy boost, consuming carbs alone often leads to sudden spikes in glucose levels, followed by energy crashes and those pesky hunger pangs.
But here's where meal sequencing comes into play. A September 2020 study revealed that consuming protein and/or fat before carbohydrates triggers the secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). This hormone not only reduces the secretion of insulin and glucagon but also improves postprandial glucose responses. GLP-1 has the added benefit of suppressing appetite by delaying gastric emptying, keeping you feeling full for longer periods. By sequencing your meals strategically, you can potentially improve glucose swings and maintain more stable values throughout the day.
The Potential Benefits of Meal Sequencing
Now, let's explore the potential benefits of meal sequencing, starting with fat loss. Satiety plays a crucial role in any weight loss journey. The goal is to feel satisfied while shedding those extra kilos. By preventing significant glucose swings, meal sequencing not only aids in glucose control but also helps regulate hunger. A study conducted in April 2021 found that dips in glucose levels after a meal predicted subsequent hunger and energy intake. So, maintaining steady glucose levels can keep hunger at bay and reduce overall energy intake.
When it comes to avoiding blood sugar spikes that can damage blood vessels, the order in which you eat matters. Consuming carbohydrates on their own leads to rapid glucose absorption, causing a quick rise and subsequent drop in glucose levels. However, adding other nutrients such as fiber, protein, or fat to your meal can slow down the digestion of glucose. This means that glucose is absorbed more gradually, resulting in a gentler rise and longer-lasting energy. By preventing high glucose spikes, you can reduce the risk of microvascular and endothelial damage, as well as oxidative stress. Avoiding repeated exposure to high glucose values is crucial in preventing cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis.
A pilot study from July 2015 demonstrated that consuming protein and fiber before carbs resulted in significantly lower postprandial glucose and insulin levels compared to the reverse order. This decrease in insulin secretion suggests that meal patterns can improve insulin sensitivity. In other words, the timing of carb ingestion during a meal is just as important as the content of the meal itself. This newfound understanding challenges traditional restrictive diets that solely focus on "how much" and "what to eat."

Now that you understand the importance of meal sequencing, let's discuss some practical tips and tricks you can incorporate into your daily routine:
- Eat Your Protein First: Consuming protein before carbs helps your body tolerate carbs better. For example, try eating eggs before pancakes or having several pieces of chicken before rice. Snack on protein/fat combinations like boiled eggs, edamame, nut butter, cheese, avocado, or tofu.
- Start Your Meals With a Salad: Incorporating fiber-rich foods into your meals slows down carb digestion, preventing rapid rises and falls in glucose levels. Include non-starchy vegetables like cauliflower, greens, asparagus, eggplant, mushrooms, cabbage, and radishes. Also, make sure to include natural sources of fiber in every meal, such as raspberries, apples, strawberries, quinoa, lentils, and black beans.
- Consume a Handful of Nuts Before Your Meals: Foods that contain protein, fiber, and healthy fats provide long-lasting energy and help maintain satiety levels. Enjoy a handful of nuts like pecans, walnuts, macadamia nuts, or hazelnuts. Other options include olives, cold cuts, and peppers, as well as plain full-fat Greek yogurt.
Meal sequencing is a simple yet effective method to improve postprandial glucose levels, manage energy consumption, and support weight loss goals. By applying these practical tips to your eating habits, you can experience the benefits firsthand and reflect on your own journey towards better health. So, remember, it's not just about what you eat, but also the order in which you eat it.