How Your Hunger Hormones Control Weight Loss: A Deep Dive

Ever wondered why sometimes you're ravenous and other times you can't even look at food?
It's not just about how much you've eaten or how long it's been since your last meal. Your hunger hormones play a significant role in this dance of appetite.
Let's dive deep into the world of leptin and ghrelin, the unsung heroes (or villains) of our dietary tales.
Leptin and Ghrelin: Not Just Characters from Tolkien
While they might sound like they've been plucked straight out of Middle Earth, leptin and ghrelin are crucial hormones that influence our hunger and fullness cues.
Ghrelin, often dubbed the "hunger hormone," is secreted by your stomach when it's empty, signaling to your brain that it's time to eat. It peaks just before you eat and drops about an hour post-meal.
Leptin, derived from the Greek word for "thin," is the satiety hormone. Produced by our fat cells, it tells our brain when we've had enough to eat, allowing our body to start burning fat for energy. In a perfectly working body, ghrelin tells us to eat so we don’t die of starvation, and leptin tells us when to stop.
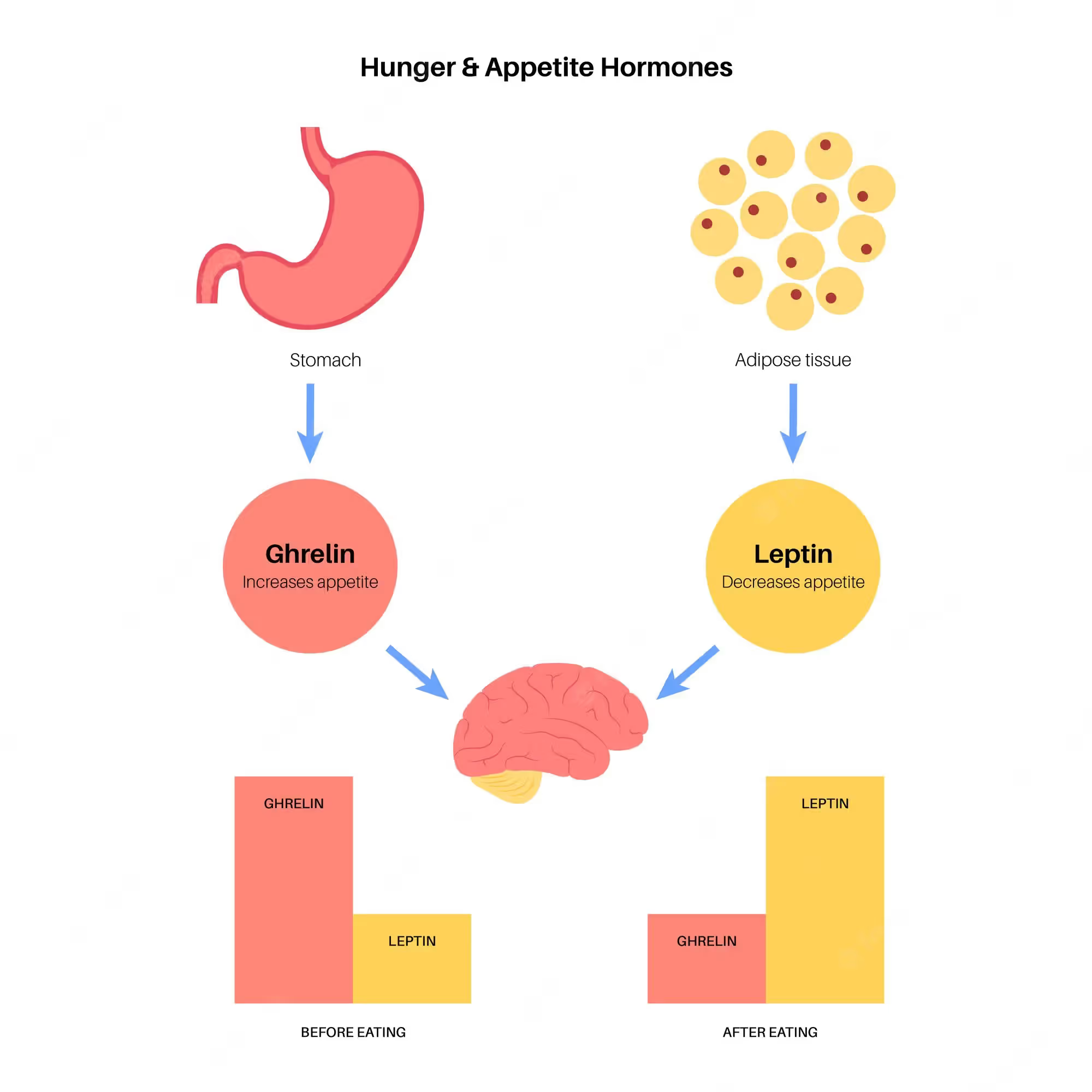
However, life isn't always this straightforward. Factors like obesity, genetics, diet, sleep quality, and lifestyle can disrupt this balance, affecting how our hunger hormones function.
Understanding Leptin
Leptin's primary role is to signal when you've had enough to eat.
It's like the responsible friend who tells you when it's time to stop at a buffet.
When leptin functions correctly, it not only helps with weight management but also supports mood regulation, memory, and mental sharpness. However, when it's off-kilter, it can lead to obesity, mood swings, and brain fog.
Leptin Resistance: The Silent Saboteur
With more fat cells comes more leptin.
However, constant exposure to high leptin levels can lead to leptin resistance, making the brain think you're still hungry.
This vicious cycle of increasing leptin resistance and obesity can be challenging to break. But , there are ways to combat this, such as consuming healthy fats, eliminating added sugars, ensuring adequate sleep, and engaging in moderate aerobic exercise.
Ghrelin: The Hunger Instigator
Ghrelin is the hormone that makes your stomach growl in the middle of a meeting.
It's the one that nudges you to grab a snack.
While it's essential for survival, in some people, especially those with obesity, ghrelin doesn't decrease as much after eating, leading to overeating.
Optimizing Ghrelin Functioning
To keep ghrelin in check, consider avoiding sugars and high-fat- sugar combination foods, consuming healthy carbs, fiber and lean proteins, getting adequate sleep, and staying hydrated.
A full stomach turns down the ghrelin signal.
7 Essential Tips to Balance Leptin and Ghrelin
Here are seven actionable tips to help you balance these hormones and combat leptin resistance:
- Incorporate Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Foods rich in omega-3s, like salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts, can help increase leptin sensitivity. They also reduce inflammation, which can be a contributing factor to leptin resistance.
- Limit Processed Foods: Highly processed foods, especially those high in sugars and unhealthy fats, can disrupt the balance of leptin and ghrelin. Focus on whole foods and a balanced diet to keep these hormones in check.
- Mindful Eating: Pay attention to your body's hunger and fullness cues. Eating slowly and savoring each bite can help you recognize when you're truly full, ensuring you don't overeat.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances, including disruptions in leptin and ghrelin. Find stress-reducing techniques that work for you, such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises.
- Avoid Late-Night Snacking: Eating late at night can interfere with the natural rhythms of leptin and ghrelin. Try to finish eating a few hours before bedtime to give these hormones a chance to regulate overnight.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity, especially strength training, can improve leptin sensitivity. It also helps regulate appetite and boosts metabolism.
- Consistent Sleep Patterns: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night. A consistent sleep schedule helps regulate leptin and ghrelin, ensuring they function optimally.
In Conclusion
If you feel your hunger hormones might be playing tricks on you, consider consulting with an endocrinologist. They can provide insights into your health, diet, and lifestyle, guiding you towards optimal hormonal balance.
Remember, maintaining regular eating patterns and understanding these hormones can be the key to thriving in your health journey. After all, knowledge is power, and understanding our bodies better equips us to face life's dietary challenges head-on.
Stay nourished, stay informed, and always thrive!