Unlocking the Secrets of Metabolism: How Genetics and Environment Shape Your Body
Maintaining a healthy weight is a critical component of overall health, with the importance of weight management increasing as obesity rates continue to rise worldwide.
While lifestyle factors such as diet and physical activity undoubtedly play a significant role in weight management, recent research has highlighted the impact of genetics on metabolism and body weight.
In this article, we will explore the role of genetics in metabolism and body weight. We will begin by defining metabolism and discussing the factors that influence it, including genetics. We will then delve into the genetics of metabolism, exploring genetic variations that impact specific metabolic processes, such as fat storage and insulin sensitivity.
Additionally, we will discuss how environmental factors can influence gene expression related to metabolism and body weight, as well as strategies for managing metabolism and body weight in light of genetic and environmental factors.
By understanding the role of genetics in metabolism and body weight, we can take a more personalized approach to weight management and make informed decisions about lifestyle modifications and medical interventions.
The Basics of Metabolism
Metabolism refers to the chemical processes that occur within the body to maintain life, including the conversion of food into energy and the elimination of waste. Two main types of metabolism exist catabolism and anabolism.
Catabolism is the process of breaking down molecules in the body to release energy. During catabolism, enzymes break down macronutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into smaller molecules that can be used to produce energy. This energy is used by the body for activities such as movement, digestion, and maintaining body temperature.
Anabolism, on the other hand, is the process of building up molecules in the body. During anabolism, molecules are synthesized from smaller components to create larger molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids. This process requires energy and is responsible for the growth and repair of tissues and organs in the body.
The rate at which metabolism occurs is influenced by several factors, including age, sex, body size and composition, and physical activity level. Additionally, genetics can play a significant role in metabolic processes, impacting an individual's susceptibility to weight gain and other health issues.
The Genetics of Metabolism
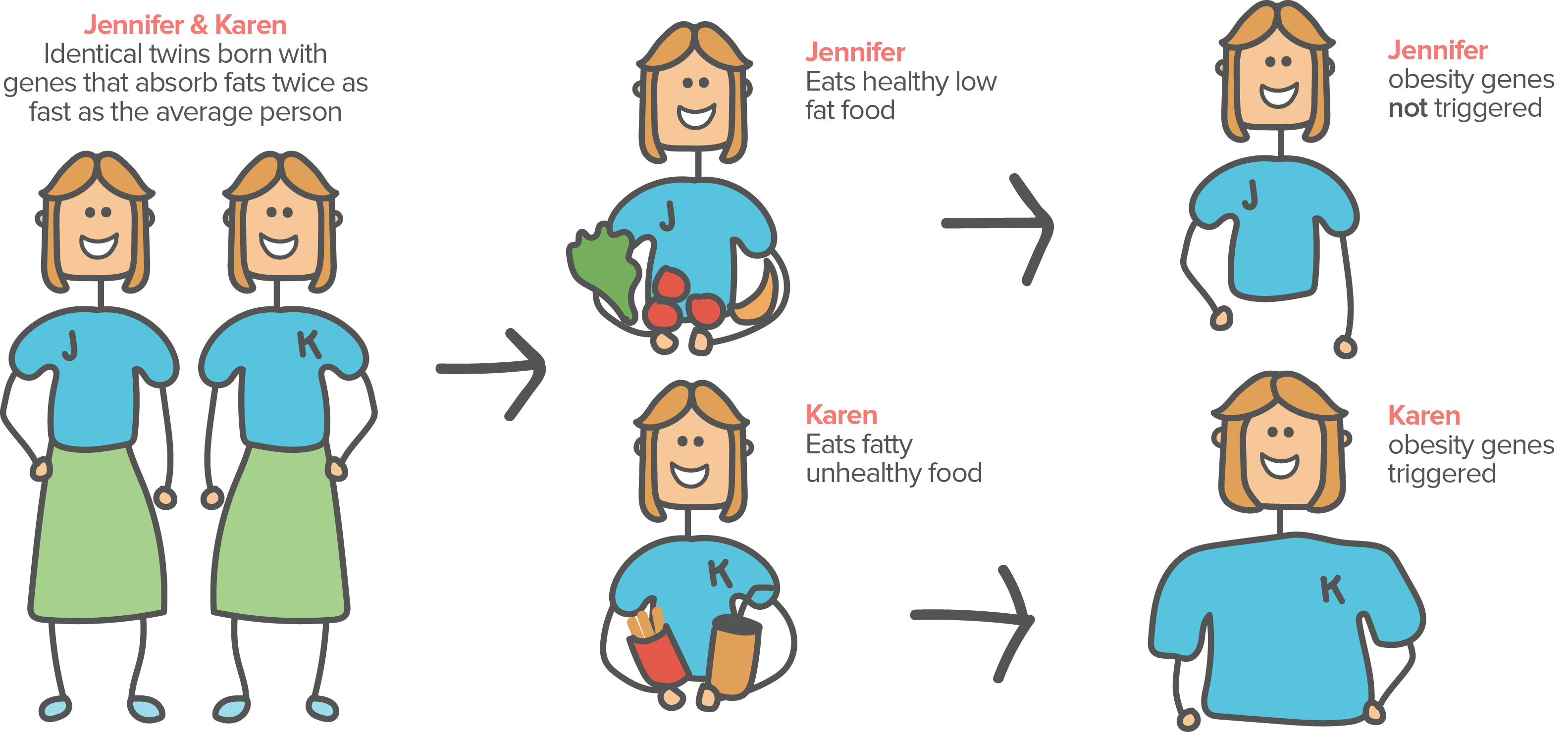
Genetic Variations that can Impact Metabolism and Body Weight
While genetics do not solely determine an individual's metabolism and body weight, they can have a significant impact. Researchers have identified several genetic variations that can influence an individual's metabolism and weight, including variations in genes related to fat storage, appetite regulation, and insulin sensitivity.
How Genetic Variations Impact Specific Metabolic Processes, Such as Fat Storage and Insulin Sensitivity
Genetic variations related to fat storage impact how the body stores and uses fat. For example, some individuals may have a genetic variation that results in the body storing more fat, leading to a higher risk of obesity. Additionally, genetic variations related to insulin sensitivity impact how the body uses glucose for energy, with individuals who have decreased insulin sensitivity being at a higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes.
The Role of Environmental Factors

While genetics play a significant role in metabolic processes and body weight, environmental factors can also impact gene expression related to metabolism and weight. These factors include diet, physical activity, stress, and exposure to toxins and pollutants.
Diet is one of the most significant environmental factors impacting metabolism and weight. Consuming a diet high in processed foods and added sugars can lead to changes in gene expression related to metabolism, potentially leading to weight gain and metabolic dysfunction. Conversely, consuming a diet rich in whole, nutrient-dense foods can support healthy gene expression and metabolic function.
Physical activity is also a crucial environmental factor impacting metabolism and weight. Regular exercise can increase metabolic rate, improve insulin sensitivity, and support healthy weight management. On the other hand, a sedentary lifestyle can lead to metabolic dysfunction and weight gain.
Stress is another environmental factor that can impact metabolism and weight. Chronic stress can lead to changes in hormones related to appetite regulation and fat storage, potentially leading to weight gain and metabolic dysfunction.
Finally, exposure to toxins and pollutants in the environment can also impact metabolic function and weight. These toxins can disrupt hormones related to metabolism and lead to metabolic dysfunction and weight gain.
By understanding how environmental factors impact gene expression related to metabolism and weight, individuals can make informed decisions about their diet and lifestyle to support healthy metabolic function and weight management.
Strategies for Managing Metabolism and Body Weight
Managing metabolism and body weight can be challenging, given the complex interplay between genetic and environmental factors. However, several strategies can support healthy metabolic function and weight management, including:
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a balanced diet that includes a variety of whole, nutrient-dense foods can support healthy metabolic function and weight management.
- Regular Physical Activity: Regular physical activity can increase metabolic rate, improve insulin sensitivity, and support healthy weight management.
- Stress Management: Practicing stress management techniques, such as mindfulness meditation and yoga, can help reduce chronic stress and support healthy metabolic function.
- Toxin and Pollutant Reduction: Reducing exposure to toxins and pollutants in the environment can support healthy metabolic function and weight management.
- Behavioral Therapy: Behavioral therapy, such as dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), can help individuals identify and change unhealthy eating behaviors and thought patterns related to food and weight.
By incorporating these strategies into a comprehensive approach to metabolism and weight management, individuals can support healthy metabolic function and achieve their weight management goals.
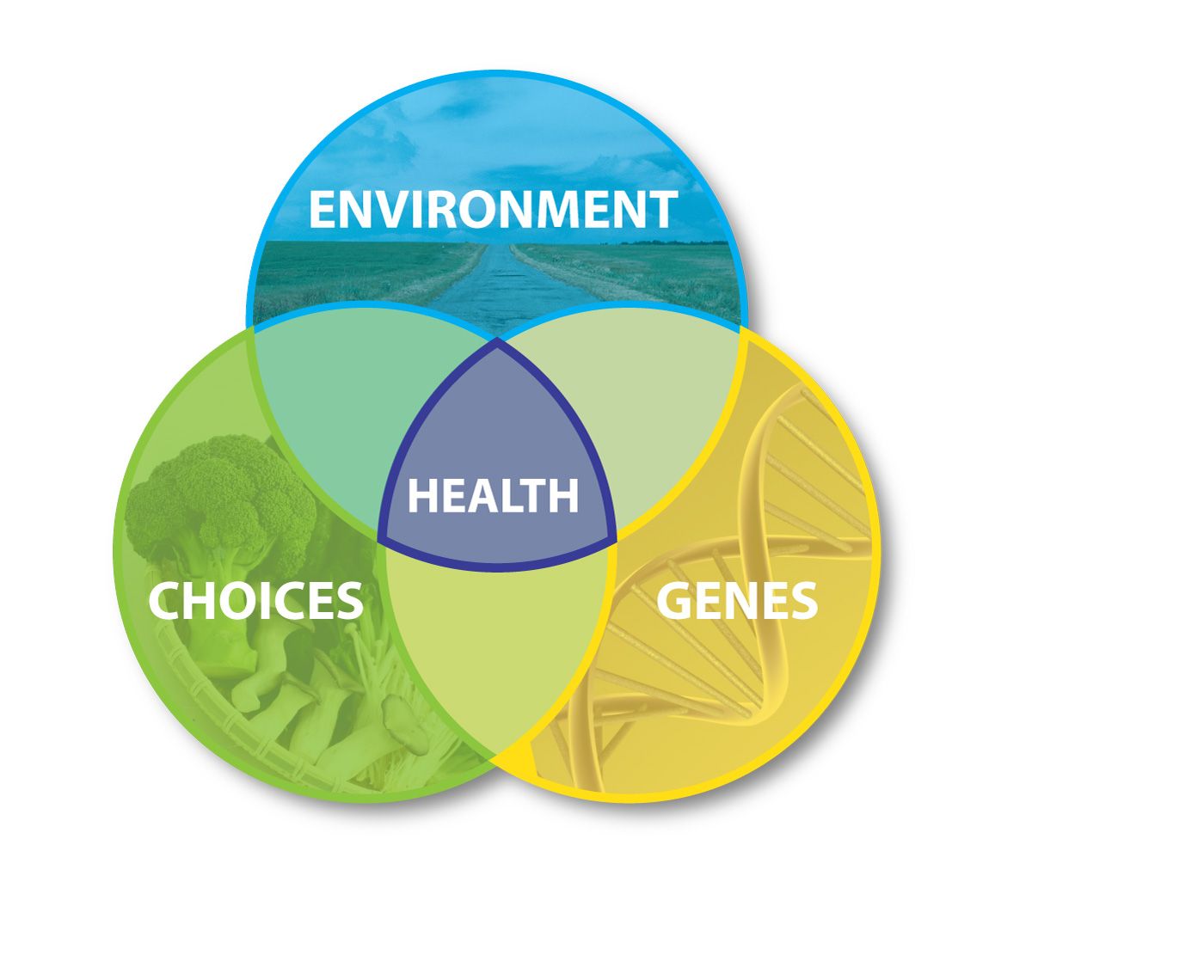
While genetics play a significant role in metabolic processes and body weight, environmental factors can also impact gene expression related to metabolism and weight. By understanding how genetics and environmental factors impact metabolic function and weight, individuals can make informed decisions about their diet and lifestyle to support healthy metabolic function and weight management.
It is essential to understand that genetics and environmental factors both play significant roles in metabolic function and weight management. By taking a personalized approach that considers individual genetic variations and environmental factors, individuals can support healthy metabolic function and achieve their weight management goals.
It is also important to recognize the potential impact of environmental factors on gene expression related to metabolism and weight. Making informed decisions about diet, physical activity, stress management, and toxin reduction can support healthy metabolic function and weight management.
If you're struggling to manage your metabolism and body weight, don't hesitate to reach out to me for help. As a dietitian and psychologist, with expertise in obesity, eating disorders, and mental health disorders. I can provide personalized support and guidance to help you achieve your goals. Contact me today to learn more!