The Dopamine Chase: How Pursuing Pleasure Can Lead to Unhealthy Habits

Explanation of dopamine and its role in the brain Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in the brain's reward and motivation system. It is released in response to pleasurable experiences, such as food, sex, and social interaction, and is responsible for the feelings of pleasure and satisfaction we associate with these activities. Dopamine also plays a role in motor control and cognitive function and has been linked to a variety of mental health disorders, including addiction and depression.
This deep-dive will explore how dopamine works in the brain, and how it motivates us to seek out rewards and engage in certain behaviors. We will discuss common dopamine-seeking behaviors, such as social media use and food cravings, and offer tips for becoming aware of our own dopamine habits.
Finally, we will provide strategies for developing healthy dopamine habits and creating positive feedback loops to promote lasting behavior change. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of how dopamine affects your behavior, and how to harness its power to make positive changes in your life.
Explanation of how dopamine is produced and released in the brain.
Dopamine is produced by neurons in several regions of the brain, including the substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area (VTA), and hypothalamus. Once produced, dopamine is stored in vesicles and released into the synaptic cleft in response to a variety of stimuli. These stimuli can include both internal cues, such as hunger or thirst, and external cues, such as the sight or smell of food. Once released, dopamine binds to receptors on nearby neurons, triggering a cascade of biochemical reactions that ultimately lead to feelings of pleasure and reward.
Dopamine's role in reward processing and motivation
Dopamine is often referred to as the brain's "reward chemical," as it plays a crucial role in the brain's reward processing and motivation system. When we engage in activities that are pleasurable or rewarding, such as eating a delicious meal or spending time with loved ones, dopamine is released in the brain. This release of dopamine reinforces the behavior, making it more likely that we will engage in it again in the future.
The dopamine pathway and its effects on behavior
The dopamine pathway refers to a network of brain regions and neural connections that are involved in the production, release, and regulation of dopamine. This pathway includes the VTA, which is responsible for producing and releasing dopamine, as well as the nucleus accumbens, prefrontal cortex, and amygdala, which are involved in reward processing and decision-making. Activation of the dopamine pathway can lead to a variety of behavioral effects, including increased motivation, decreased pain sensitivity, and enhanced attention and focus. However, overstimulating the dopamine pathway can also lead to addictive behaviors and compulsive habits.
The dopamine chase

Common dopamine-seeking behaviors
Many of our daily habits and behaviors are driven by our desire for dopamine. For example, checking social media, watching TV, and indulging in unhealthy foods can all trigger dopamine release in the brain. While these activities may provide temporary pleasure, they can also lead to negative consequences, such as addiction, poor health, and decreased productivity.
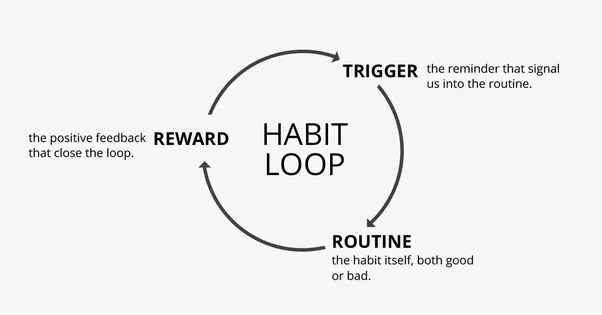
Explanation of the cycle of craving and reward
The cycle of craving and reward refers to the process by which we seek out and engage in dopamine-releasing activities. When we encounter a cue that is associated with a pleasurable experience, such as the smell of our favorite food or a notification on our phone, our brain releases dopamine in anticipation of the reward. This dopamine release creates a craving for the reward, which motivates us to seek it out. When we finally receive the reward, dopamine is released again, reinforcing the behavior and making it more likely that we will engage in it again in the future.
The downside of the dopamine chase
While dopamine is an important neurotransmitter that helps us experience pleasure and motivation, the constant pursuit of dopamine can also have negative consequences. Engaging in activities that provide quick dopamine hits, such as scrolling through social media or binge eating, can lead to addictive behaviors and decreased self-control. Additionally, constantly seeking out dopamine can make it difficult to find pleasure in other activities, leading to a sense of emptiness or dissatisfaction.
Tips for becoming aware of your own dopamine habits
To break free from the cycle of craving and reward, it's important to become aware of your own dopamine-seeking behaviors. Take note of the activities that provide quick dopamine hits, and consider how they may impact your overall health and well-being. This awareness can help you make more intentional choices about how you spend your time and energy.
Strategies for creating healthy dopamine habits
Rather than relying on unhealthy habits to get your dopamine fix, consider developing new, healthy dopamine habits. Engage in activities that provide natural dopamine boosts, such as exercise, spending time in nature, and engaging in hobbies you enjoy. By creating positive feedback loops around healthy behaviors, you can retrain your brain to seek out more sustainable sources of pleasure and motivation.
Identifying our own dopamine habits

How to recognize dopamine-seeking behaviors
To identify your own dopamine-seeking behaviors, it's important to pay attention to your thoughts and actions throughout the day. Notice which activities you engage in when you're feeling bored, stressed, or anxious, and consider how these behaviors may be impacting your overall well-being. You may also want to track your behaviors over time to identify patterns and triggers.
Common dopamine-seeking behaviors to look out for
Some common dopamine-seeking behaviors include:
- Scrolling through social media
- Binge-watching TV
- Eating unhealthy foods
- Shopping excessively
- Engaging in risky behaviors
- Seeking out attention or validation from others
- Engaging in compulsive habits, such as nail-biting or skin-picking.
How to assess the impact of your dopamine habits
Once you've identified your dopamine habits, it's important to assess how they may be impacting your overall health and well-being. Consider the physical, mental, and emotional consequences of these habits, and ask yourself whether they align with your long-term goals and values. If your dopamine habits are causing negative consequences, it may be time to make a change.
Tips for breaking free from unhealthy dopamine habits

Breaking free from unhealthy dopamine habits can be challenging, but it is possible with time and effort. Here are a few tips to get started:
- Replace unhealthy habits with healthier alternatives, such as exercise, meditation, or spending time with loved ones.
- Set realistic goals and track your progress over time.
- Seek support from friends, family.
- Practice self-compassion and forgiveness if you slip up.
By creating healthier dopamine habits, you can improve your overall health and well-being, reduce stress and anxiety, and increase your productivity and focus. Additionally, by breaking free from the cycle of craving and reward, you can experience more sustained feelings of pleasure and happiness in your daily life.
Creating new dopamine habits
Understanding the science behind creating new habits
Creating new dopamine habits involves creating new neural pathways in the brain. These pathways become stronger with repetition and can eventually become automatic behaviors. It takes time and effort to establish new habits, but with consistent practice, you can create healthier habits that lead to long-term well-being.
Setting goals and creating a plan
To create new dopamine habits, it's important to set specific goals and create a plan for achieving them. Consider what new behaviors you want to adopt and why, and then break them down into smaller, achievable steps. This will help you stay motivated and on track.
Finding healthy dopamine sources
To create new dopamine habits, you'll need to find healthy sources of dopamine that align with your goals and values. This might involve engaging in new activities that challenge you, such as learning a new skill or trying a new hobby. It might also involve seeking out positive social interactions or spending time in nature.
Incorporating Mindfulness and Self-reflection
To create sustainable new habits, it's important to incorporate mindfulness and self-reflection into your daily routine. This means being aware of your thoughts and emotions and reflecting on how your behaviors impact your overall well-being. Mindfulness practices such as meditation and deep breathing can help you stay grounded and focused on your goals.
Celebrating your successes and learning from your failures
Creating new dopamine habits is a journey, and it's important to celebrate your successes along the way. Acknowledge the progress you've made and the hard work you've put in. At the same time, be kind to yourself if you experience setbacks or failures. Use these experiences as opportunities for learning and growth, and stay committed to your long-term goals.
Creating new dopamine habits involves recognizing your current behaviors, assessing their impact on your well-being, and setting goals for new, healthier habits. By incorporating mindfulness, self-reflection, and positive reinforcement, you can establish new neural pathways in your brain and experience sustained feelings of pleasure and happiness. With time and effort, you can create new dopamine habits that support your overall health and well-being.
As we wrap up, I encourage you to take some time to reflect on your own dopamine habits. Consider the behaviors and experiences that bring you pleasure and ask yourself if they align with your long-term goals and values. If you find that your current dopamine habits are not serving you well, remember that you have the power to change them.
Reflection:
- What activities or experiences do I find myself chasing after even when they have negative consequences for my health or well-being?
- When I experience stress or discomfort, what behaviors or activities do I turn to for comfort or relief?
- Do my current dopamine habits align with my long-term goals and values?
- How do my current dopamine habits impact my relationships with others?
- What steps can I take to create healthier dopamine habits that support my overall health and well-being?