Deep Dive into Omega-3: Navigating Its Impact on Mind and Body

"The food you eat can be either the safest and most powerful form of medicine or the slowest form of poison." - Ann Wigmore
These essential fats, notably found in marine life, nuts, and seeds, have long been celebrated for their myriad health benefits, from safeguarding our hearts to bolstering our brains. But how exactly do these fats, particularly those derived from the depths of our oceans, wield such profound influence over our well-being?
Omega-3s: The Unsung Heroes of Cellular Communication
Omega-3 fats, specifically ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), and EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), are not merely components to be metabolized for energy. They are integral to the very structure and function of our cells, influencing cellular communication, hormone production, and even the integrity of our brain and nerve tissues.
The fats we consume become embedded in our cellular architecture, influencing processes from inflammation to neurotransmission, thereby impacting our moods, cognitive function, and overall mental health.
The Omega-3 and Depression: A Ray of Light in the Darkness
Recent research has illuminated the potential of Omega-3s, particularly EPA and DHA, in mitigating depressive disorders.
A study conducted by the National Institute of Health Research has unveiled that high doses of Omega-3 fatty acids may provide relief from depression by leveraging their anti-inflammatory properties.
The study, which involved both laboratory and patient research, demonstrated how Omega-3s generate anti-inflammatory effects in hippocampus cells, a region of the brain pivotal for learning, memory, and emotional regulation.
The research revealed that Omega-3s, specifically their metabolites, could decrease cell death and enhance cell generation in the hippocampus, offering potential pathways for developing new treatments for depression.
The study also highlighted a correlation between higher levels of these metabolites and reduced depression scores in patients, providing a beacon of hope in the exploration of Omega-3s as a potential therapeutic ally in mental health management.

Beyond Depression: The Multifaceted Impact of Omega-3s
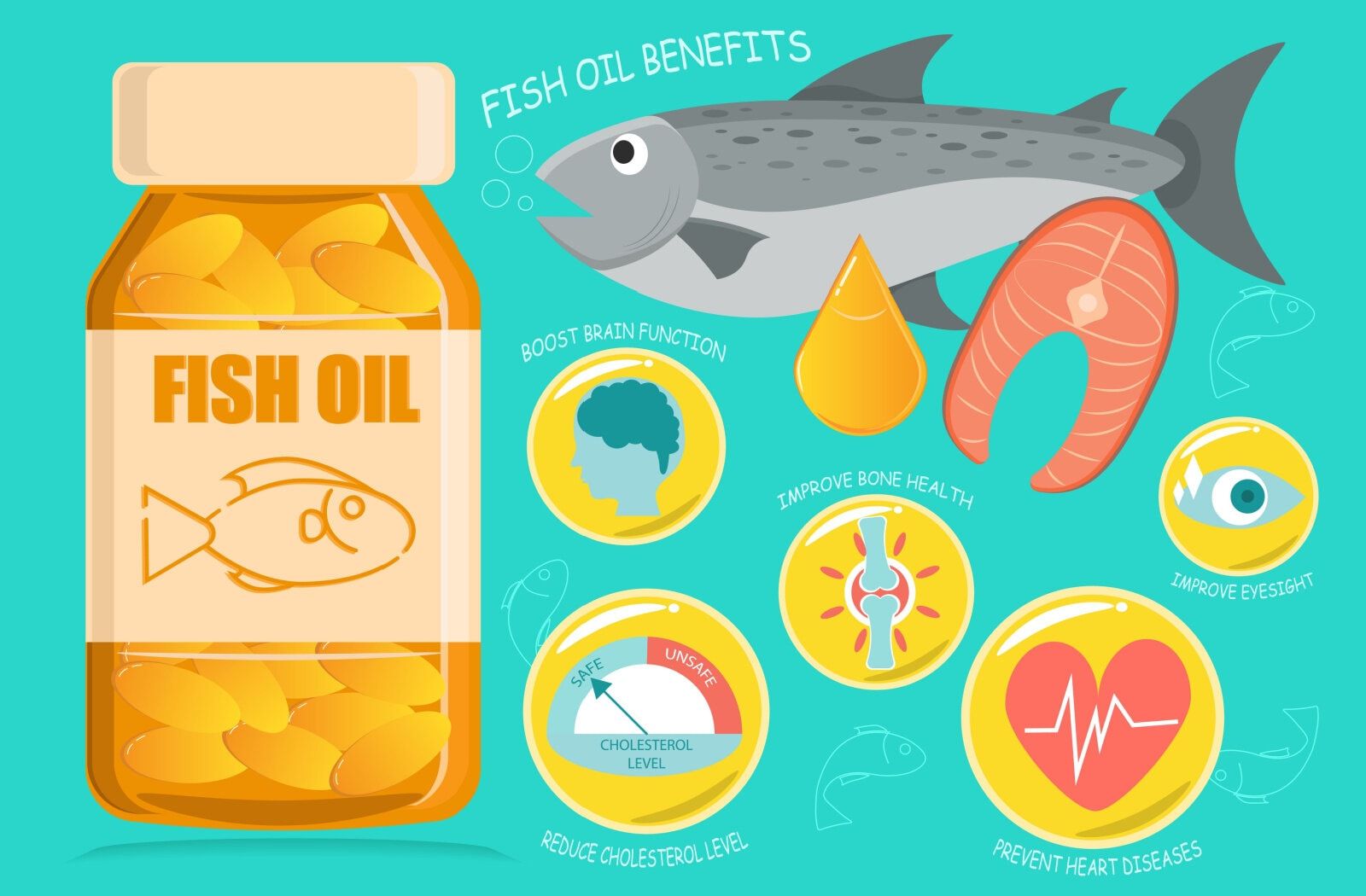
Omega-3s are not merely potential warriors in the battle against depression. Their influence permeates various aspects of our health, including:
- Heart and Brain Health: Omega-3s have been linked to reduced risks of heart diseases and may safeguard our brains against aging and neurodegenerative disorders.
- Inflammation Reduction: These fats can modulate our inflammatory responses, which is crucial given the established links between chronic inflammation and numerous health conditions, including mental health disorders.
- Cellular Communication: Omega-3s influence cellular signaling, impacting processes from blood vessel constriction to pain perception.
- Metabolic Regulation: These essential fats can also influence our metabolic health, potentially aiding in maintaining a healthy body weight and supporting muscle growth.
Omega-3 Essentials: Sourcing and Dosage in Our Diets
Embarking on a journey with Omega-3s necessitates a fundamental understanding of their sources and the optimal dosages to reap their myriad benefits, particularly in the realms of mental well-being and inflammation management.
Where to Find Omega-3s in Your Diet
Omega-3 fatty acids, specifically ALA, DHA, and EPA, can be sourced from a variety of foods:
- Marine Life: Cold-water fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in DHA and EPA.
- Nuts and Seeds: Flax seeds, chia seeds, and walnuts contain ALA, which can be converted to DHA and EPA, albeit inefficiently so not the best option.
- Algae: Certain algae offer plant-based DHA, providing a viable option for those adhering to vegetarian or vegan diets.
Determining Your Omega-3 Needs
The optimal dosage of Omega-3s, particularly EPA and DHA, can be influenced by various factors, including dietary habits, health conditions, and specific health goals.
- General Population: For the average individual without depressive symptoms, aiming for a combined EPA and DHA intake of 600mg per day is a practical target. This could be achieved by consuming approximately three servings of fatty fish per week.
- Individuals with Depression and Inflammation: For those navigating through depression or dealing with inflammation, a higher dosage of approximately 1000mg of combined EPA and DHA may be beneficial. This might necessitate more frequent consumption of Omega-3-rich foods or considering supplementation.
Supplementing Wisely

If your dietary intake of Omega-3s is insufficient or if you require higher dosages, supplements can be a practical option. When choosing an Omega-3 supplement, consider the following:
- Quality: Ensure the supplement is sourced from reputable manufacturers and is free from contaminants.
- Concentration: Check the EPA and DHA content per serving to ensure it meets your dosage requirements.
- Form: Omega-3s are available in various forms, including fish oil, krill oil, and algae oil, catering to different dietary preferences and requirements.
Here are four brands of Omega-3 supplements that I personally trust and utilize:
- Biogen Supreme Omega 60
- Solal Krill Oil Omega 3
- Wellvita Omega 3 1000mg
- Metagenics Omegagenics Epa Dha 720
Why Combining Omega-3 and Omega-6 Supplements Is Not Be Beneficial
In the vast sea of nutritional supplements, products combining Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids often surface, marketed as a convenient solution to meet your essential fatty acid needs. However, delving deeper into the science of these fats reveals why purchasing them together might not be the optimal choice.
Understanding the Omega Balance
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: As we’ve explored, these are crucial for reducing inflammation, supporting brain health, and potentially alleviating symptoms of depression and other mental health conditions.
- Omega-6 Fatty Acids: Predominantly found in vegetable oils, nuts, and seeds, Omega-6s are essential but are also pro-inflammatory when consumed in excess increases inflammation.
The Delicate Balance: Omega-3 vs. Omega-6
- Ratio Matters: The balance between Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids in our diet is crucial. An ideal ratio is believed to be around 1:4 (Omega-3:Omega-6), but the typical Western diet leans heavily towards Omega-6, often reaching ratios as skewed as 1:30.
- Inflammatory Response: While Omega-6s are essential, their overabundance, especially in the absence of sufficient Omega-3s, can promote inflammation due to their pro-inflammatory properties.
Why Combining Them Might Be Counterproductive
- Negating Benefits: Given that Omega-3s and Omega-6s can have opposing effects on inflammation, combining them might diminish the anti-inflammatory benefits that Omega-3s offer, especially if your diet is already rich in Omega-6s.
- Optimal Absorption: Some studies suggest that Omega-3s and Omega-6s might compete for the same enzymes in our body during the metabolic process. Thus, consuming them together might hinder the optimal absorption and utilization of Omega-3s.
Strategizing Your Omega Intake
- Prioritize Omega-3: Given the typical abundance of Omega-6 in our diets, prioritizing Omega-3 supplementation without additional Omega-6 is often more aligned with achieving the desired balance and reaping the anti-inflammatory and mental health benefits.
- Mindful Consumption: Be mindful of your Omega-6 intake from dietary sources and consider whether additional supplementation is necessary based on your specific health needs and goals.
- Consult a Professional: Always consult healthcare professionals when considering supplementation, ensuring that your choices are tailored to your unique health profile.
Reflection and Application:
- Incorporation of Omega-3s: How can you practically incorporate more Omega-3s into your diet?
- Mindful Supplementation: If considering Omega-3 supplements, how can you ensure you choose a quality product that provides adequate EPA/DHA?
- Holistic Health: How can the knowledge of Omega-3s influence your perspective on the interconnectedness of physical and mental health?