From Understanding to Action: Taking Control of Your Cholesterol and Blood Sugar Levels

Cholesterol and blood sugar levels play significant roles in our overall health. While cholesterol is important for various bodily functions, elevated levels can lead to health issues such as heart disease. Similarly, high blood sugar levels can increase the risk of diabetes and impact cholesterol levels.
In this blog post, we will explore the relationship between cholesterol and blood sugar, discuss normal levels for both, and provide practical tips to help you maintain healthy levels.
Understanding the Relationship:
Excessive sugar consumption has been linked to conditions like diabetes, obesity, heart disease, and high cholesterol. When we consume carbohydrates, they break down into glucose, which provides energy to our cells. However, consuming too many carbs and sugars can lead to abnormally high blood sugar levels. Chronic high blood sugar levels can result in insulin resistance, which affects cholesterol levels by lowering HDL cholesterol and increasing LDL cholesterol.
Normal Levels for Cholesterol and Blood Sugar:
Monitoring cholesterol levels involves measuring LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. Lower LDL cholesterol levels are generally considered healthier, while higher HDL cholesterol levels are beneficial. Elevated triglyceride levels can increase the risk of a heart attack. Blood sugar levels can be measured through tests such as the A1C test, fasting blood sugar test, glucose tolerance test, or random glucose test.
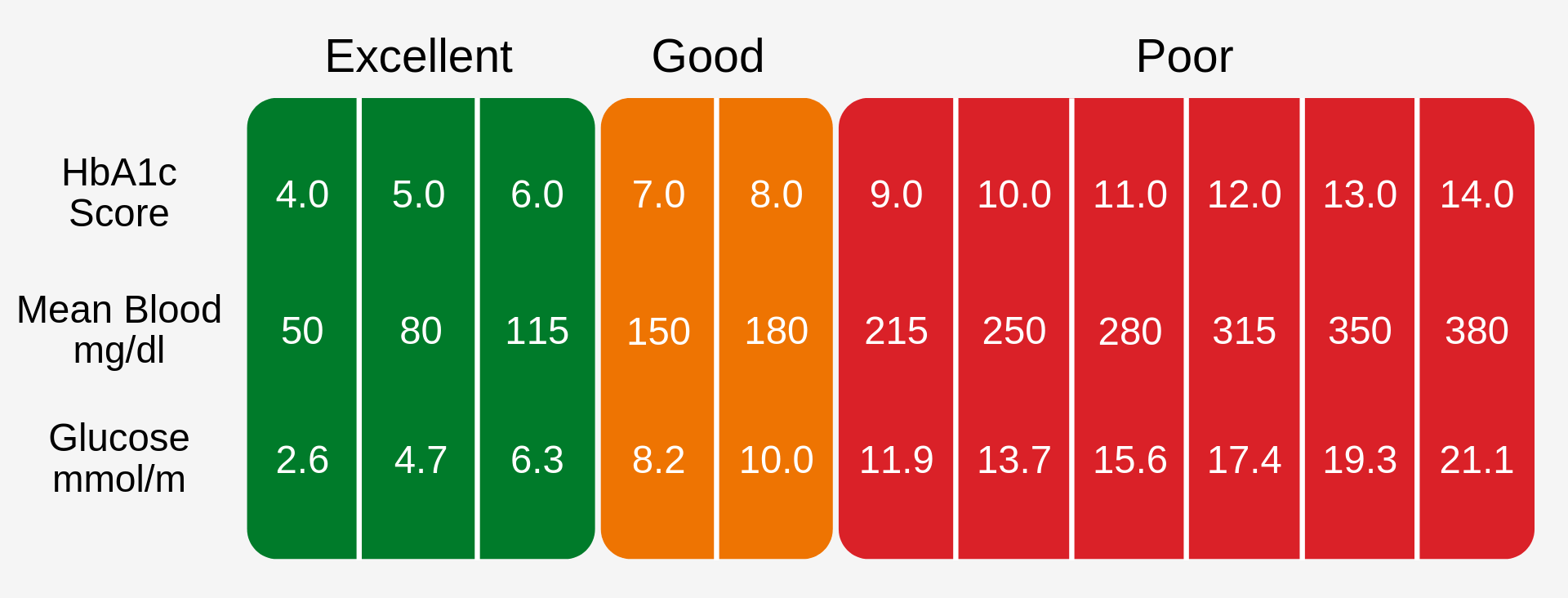
The normal range for these tests:
HbA1C: The normal range for non-Diabetic people is 4-6 mmol/l.
You're considered to be Diabetic if your fasted blood glucose (before eating breakfast) is over 7 mmol/l, or your non-fasted level is over 11 mmol/l.
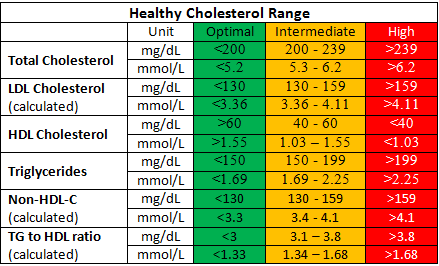
Cholesterol: For most healthy people normal cholesterol levels are: Total cholesterol LESS than 5 mmol/L. LDL cholesterol level LESS than 3 mmol/L. HDL cholesterol levels MORE than 1.2 mmol/L for women or 1.0 mmol/L for men.
The Impact of Diet on Cholesterol:
Diet plays a significant role in cholesterol management. Excessive consumption of fats and carbohydrates, particularly saturated fats and added sugars, can contribute to elevated cholesterol levels. It's important to limit the intake of saturated fats and avoid trans fats. On the other hand, incorporating foods like oats, whole grains, beans, nuts, fruits, and fatty fish into your diet can help manage cholesterol levels.
Recommended Foods for Cholesterol Management:
Include the following cholesterol-lowering foods in your diet:
- Oats
- Whole grains
- Beans
- Eggplant
- Nuts
- Vegetable oils
- Fruits
- Soy and soybeans
- Fatty fish
- Fiber
Limit the consumption of the following foods:

- Milk chocolate
- Baked goods
- Deep-fried foods
- Processed foods
- Processed meats
- Full-fat dairy
- Margarine
- Hydrogenated oils
The Role of Exercise in Managing Cholesterol Levels:
Regular exercise not only contributes to overall well-being but also helps lower cholesterol levels. Physical activity helps transport LDL cholesterol from the blood to the liver for excretion. It also positively impacts lipoproteins like HDL-C and reduces triglyceride levels. Maintaining an active lifestyle can support weight loss, heart health, and cholesterol management.
Understanding the relationship between cholesterol and blood sugar is crucial for maintaining good health. By making conscious dietary choices, such as limiting saturated fats and added sugars, and incorporating cholesterol-lowering foods, you can manage your cholesterol levels effectively. Additionally, regular exercise is key to maintaining healthy cholesterol levels. By adopting these lifestyle changes, you can improve your overall well-being and reduce the risk of heart disease and diabetes. Stay proactive and take charge of your health by prioritizing cholesterol and blood sugar management.